Customized Transitions
In this section we'll take a look at customizing transitions between screens. Let's start with a basic tabs example that looks something like this
Basic tabs
import { Navigator, Tabs } from 'navigation-components';
import { View } from 'react-native';
function MyTabs() {
return (
<Navigator>
<Tabs>
<MyScreen index={0}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>1</Text>
</MyScreen>
<MyScreen index={1}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>2</Text>
</MyScreen>
<MyScreen index={2}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>3</Text>
</MyScreen>
</Tabs>
</Navigator>
);
}
const colors = ['aquamarine', 'coral', 'rebeccapurple'];
function MyScreen({ children, index }) {
return (
<View
style={{
...screenStyle,
backgroundColor: colors[index],
}}
>
{children}
</View>
);
}
const screenStyle = {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
borderRadius: 10,
marginHorizontal: 10,
};
Interpolating over screens
We'll start with updating the size and position of our tab panels when they are inactive by updating the pageInterpolation prop for our tabs component:
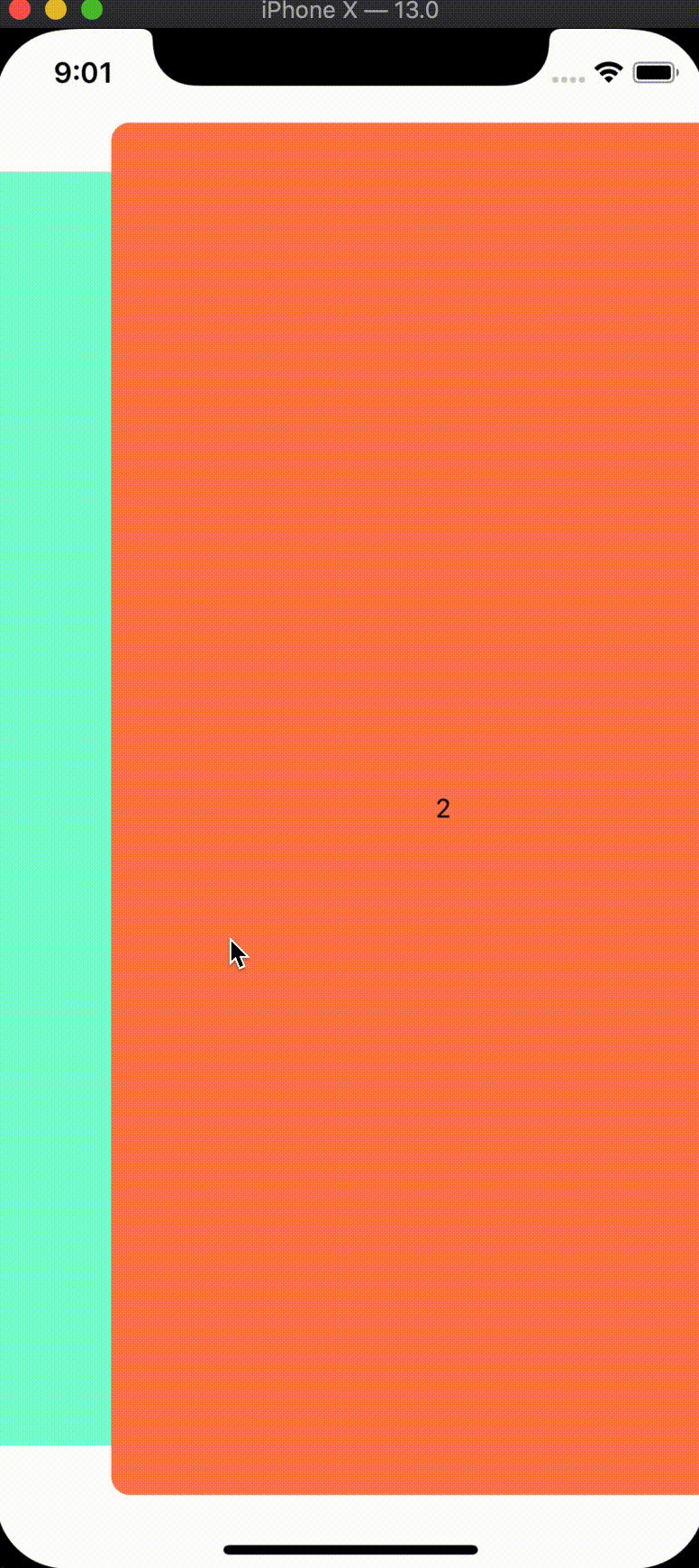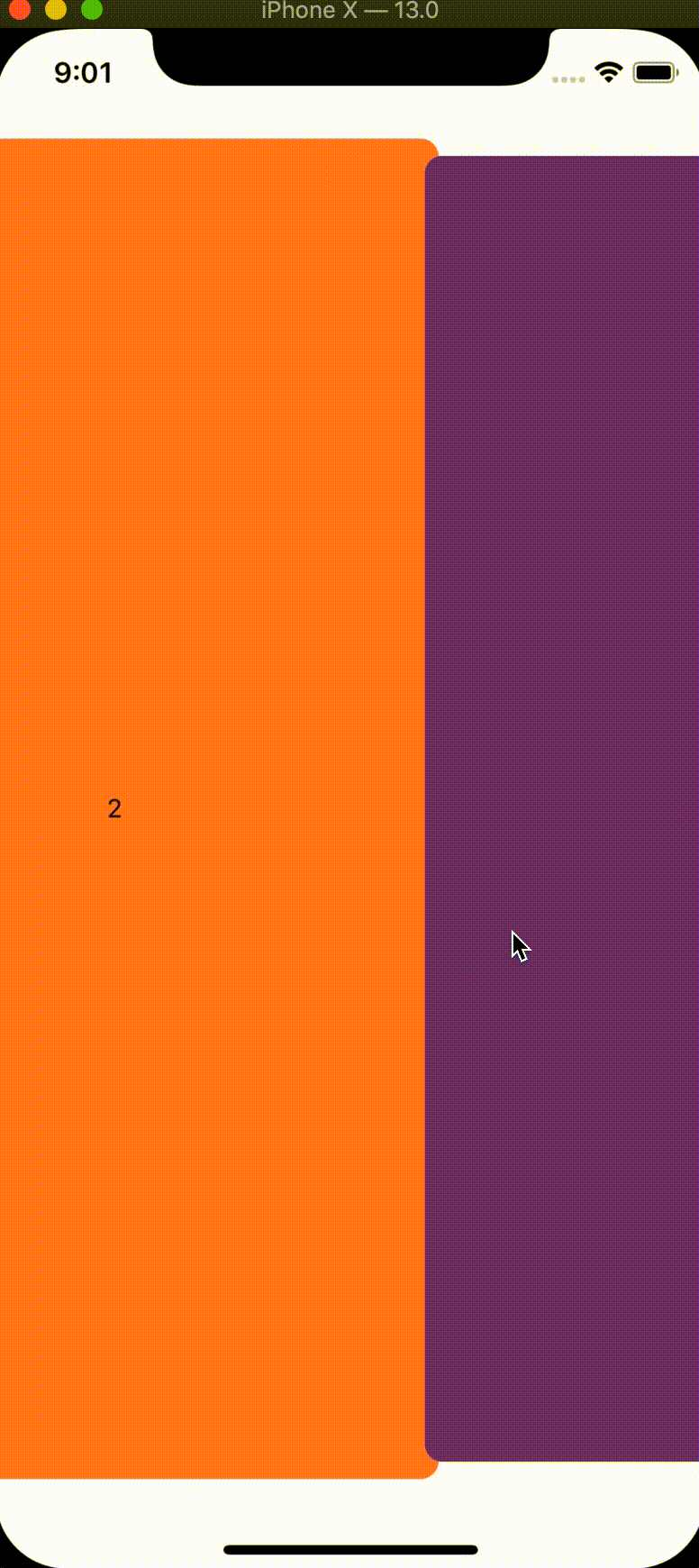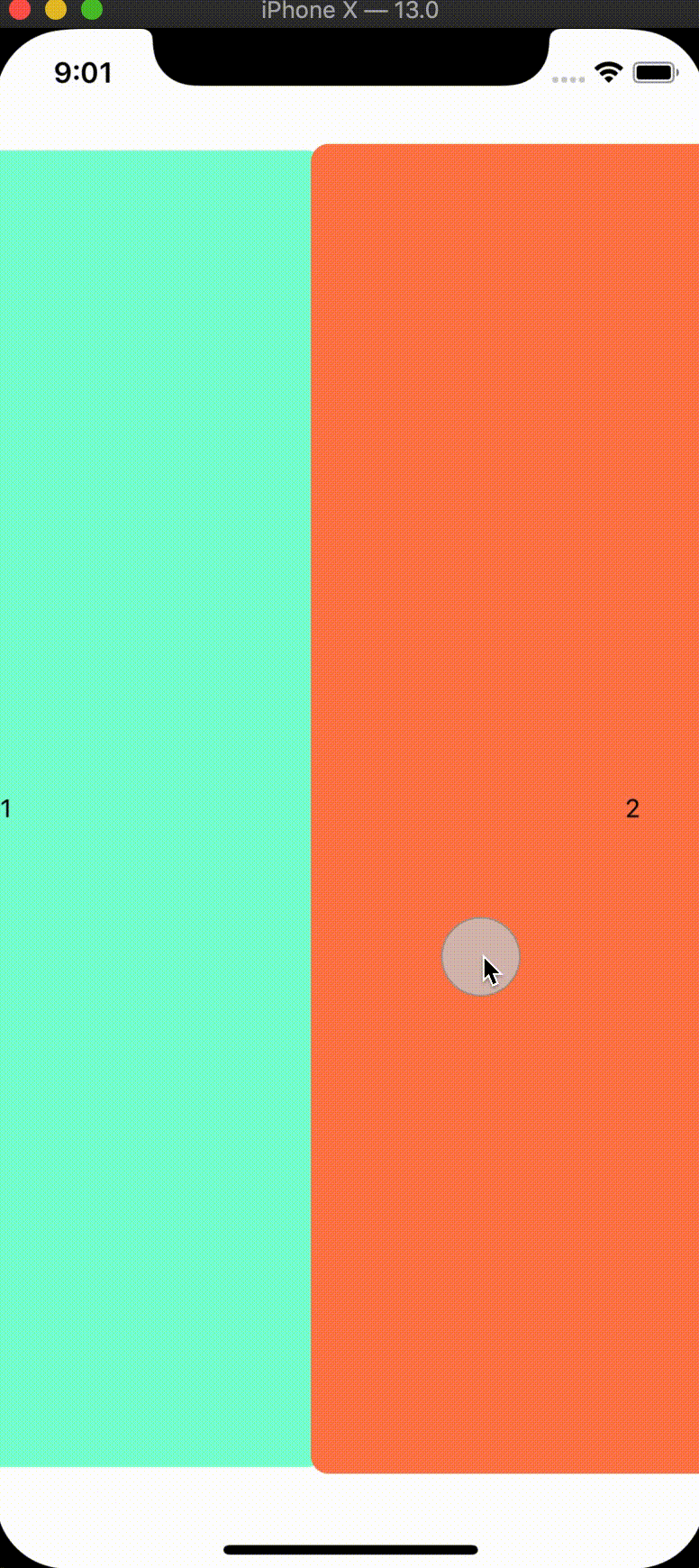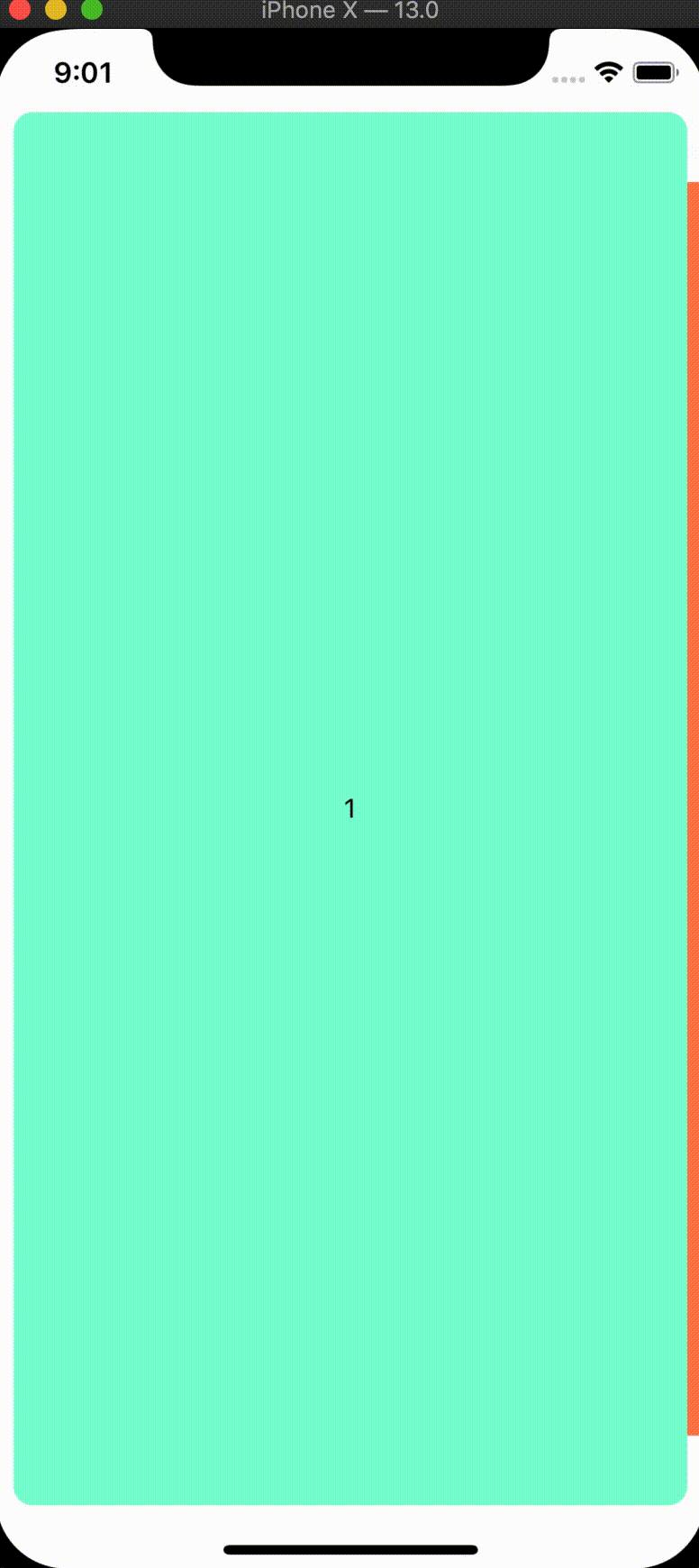
const tabInterpolation: iPageInterpolation = {
transform: [
{
translateX: {
// this will scooch screens to the left and right over by 45 points
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [45, 0, -45]
}
},
{
scale: {
// scale screens down a little bit when they are not focused
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [0.9, 1, 0.9],
},
},
],
zIndex: {
// active screen should appear over top of the others
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [-1, 2, -1]
}
};
function MyTabs() {
return (
<Navigator>
<Tabs pageInterpolation={tabInterpolation}>
{...}
</Tabs>
</Navigator>
);
}
We're able to customize any transform or zIndex properties of our tab panel based on their relative position to the active screen.
Targeting a single screen
We can target the interpolation of a single page explicitly by using the useInterpolation hook -- let's try it out:
import { useInterpolation } from 'navigation-components';
import Animated from 'react-native-reanimated';
function MySpecialScreen({ children, index }: any) {
const styles = useInterpolation({
transform: [
{
translateY: {
// move the screen vertically when its not in focus
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [-100, 0, 100],
},
},
],
});
return (
<Animated.View
style={{ ...screenStyle, ...styles, backgroundColor: colors[index] }}
>
{children}
</Animated.View>
);
}
function MyTabs() {
return (
<Navigator>
<Tabs>
<MyScreen index={0}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>1</Text>
</MyScreen>
<MySpecialScreen index={1}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>2</Text>
</MySpecialScreen>
<MyScreen index={2}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>3</Text>
</MyScreen>
</Tabs>
</Navigator>
);
}
Customizing the Tabbar
This interpolation API is shared across several different screen containers - Tabs, Stack, Modal can all take advantage of these customizations. You can even target individual Tab components if you'd like:
import {
Tabbar,
Tab,
useInterpolation,
Extrapolate,
} from 'navigation-components';
function MyTabbar() {
return (
<Tabbar>
<MyCustomTab>
<Text>1</Text>
</MyCustomTab>
<MyCustomTab>
<Text>2</Text>
</MyCustomTab>
<MyCustomTab>
<Text>3</Text>
</MyCustomTab>
</Tabbar>
);
}
function MyCustomTab({ children }: any) {
const styles = useInterpolation({
transform: [
{
scale: {
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [0.7, 1, 0.7],
extrapolate: Extrapolate.CLAMP,
},
},
],
opacity: {
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [0.7, 1, 0.7],
extrapolate: Extrapolate.CLAMP,
},
});
return (
<Tab
style={{
height: 50,
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
borderWidth: 1,
...styles,
}}
>
{children}
</Tab>
);
}
function MyTabs() {
return (
<Navigator>
<Tabs>
<MyScreen index={0}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>1</Text>
</MyScreen>
<MySpecialScreen index={1}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>2</Text>
</MySpecialScreen>
<MyScreen index={2}>
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center' }}>3</Text>
</MyScreen>
</Tabs>
<MyTabbar />
</Navigator>
);
}
useInterpolation with any component
You can use the useInterpolation hook from anywhere inside your screen components. For example, we could create an ActiveOpacity component that fades children in and out depending on the focus of the navigator:
import { useInterpolation, Extrapolate } from 'navigation-components';
import Animated from 'react-native-reanimated';
function ActiveOpacity({ index, children }: iActiveOpacity) {
const styles = useInterpolation({
opacity: {
inputRange: [-1, 0, 1],
outputRange: [0.5, 1, 0.5],
extrapolate: Extrapolate.CLAMP,
},
});
return <Animated.View style={styles}>{children}</Animated.View>;
}
Summary
Screen containers like Tabs, Stack, and Modal can be configured to control how individual screens move during transitions. The
pageInterpolationprop will target each screen inside a screen container and apply the specified transformation interpolationsuseInterpolationcan be used to target unique behaviour for individual screens in a screen container. It can also be applied to any component inside of a screen containerWe can build reusable components with
useInterpolationto capture certain UI behaviours that are relevant to the current focus of a navigator, such as a custom tab component, or an active opaciity indicator.